This article assumes that the reader is aware of the benefits of deploying a standardized backup and maintenance solution.
The solution which I’ve been promoting and deploying to all SQL Server environments (new as well as existing ones) is the award-winning SQL Server Maintenance Solution developed by Ola Hallengren and which encompasses SQL Server Backup, Integrity Check, Index and Statistics Maintenance.
The SQL Server Maintenance Solution comprises scripts for running backups, integrity checks, and index and statistics maintenance on all editions of Microsoft SQL Server 2008, SQL Server 2008 R2, SQL Server 2012, SQL Server 2014, SQL Server 2016, SQL Server 2017, and SQL Server 2019. The solution is based on stored procedures. The solution has been designed for the most mission-critical environments, and it is used in many organizations around the world. The SQL Server Maintenance Solution has been voted as Best Free Tool in the 2013, 2012, 2011, and 2010 SQL Server Magazine Awards. The SQL Server Maintenance Solution is free.
The solution is made us of a script (or alternatively available as separate scripts) which can be downloaded from https://ola.hallengren.com/ or the GitHub repository. Extensive documentation explaining the functionality and is also available.
Once downloaded, very little changes have to be applied to the script. These would be limited to the variable values in the following highlighted lines (Note: line numbers might differ between versions of the script):
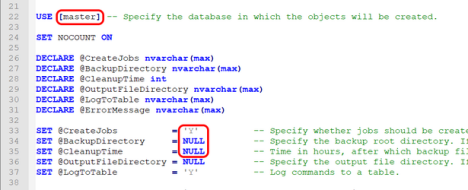
The recommendation is that the default database, currently defined as “master”, is changed to keep all database objects which are used by the solution separate from the SQL Server system objects. Personally, I like to create a DBAToolbox database using the below syntax (extracted from one of my GitHub repositories at https://github.com/reubensultana/SQLInstallConfig/) when installing and configuring a new SQL Server instance.
Create the DBAToolbox database
PRINT 'Deploying DBA Toolbox database';
DECLARE @SqlCmd nvarchar(2000);
DECLARE @device_directory nvarchar(1000);
DECLARE @compatibility_level int;
SET @device_directory = (
SELECT SUBSTRING([physical_name], 1, CHARINDEX(N'master.mdf', LOWER([physical_name])) - 1)
FROM sys.master_files WHERE [database_id] = DB_ID('master') AND [file_id] = 1);
SET @compatibility_level = (SELECT compatibility_level FROM sys.databases WHERE name = 'master');
IF NOT EXISTS (SELECT name FROM sys.databases WHERE name = N'DBAToolbox')
BEGIN
PRINT ' Creating database';
SET @SqlCmd = N'USE [master];
CREATE DATABASE [DBAToolbox] ON PRIMARY (
NAME = N''DBAToolbox'',
FILENAME = ''' + @device_directory + 'DBAToolbox.mdf'' ,
SIZE = 5120KB ,
FILEGROWTH = 1024KB )
LOG ON (
NAME = N''DBAToolbox_log'',
FILENAME = ''' + @device_directory + 'DBAToolbox_log.ldf'' ,
SIZE = 5120KB ,
FILEGROWTH = 1024KB );';
EXEC sp_executesql @SqlCmd;
EXEC sys.sp_dbcmptlevel @dbname=N'DBAToolbox', @new_cmptlevel=@compatibility_level;
ALTER DATABASE [DBAToolbox] SET RECOVERY SIMPLE;
ALTER DATABASE [DBAToolbox] SET RESTRICTED_USER;
ALTER DATABASE [DBAToolbox] SET AUTO_CLOSE OFF WITH NO_WAIT;
PRINT ' DBA Toolbox database created';
END
ELSE
PRINT 'DBA Toolbox already deployed';
-- check again...
IF NOT EXISTS (SELECT [name] FROM [sys].[databases] WHERE [name] = N'DBAToolbox')
BEGIN
RAISERROR('Database DBAToolbox does not exist!', 16, 1);
--RETURN -1;
END
PRINT ' Setting database owner for DBA Toolbox';
DECLARE @SALoginName sysname; -- login name for the 'sa'
SET @SqlCmd = '';
SET @SALoginName = (SELECT [name] FROM sys.sql_logins WHERE sid = 0x01);
SET @SqlCmd = 'USE [master];ALTER AUTHORIZATION ON DATABASE::[DBAToolbox] TO ' + @SALoginName;
EXEC sp_executesql @SqlCmd;
PRINT '
********************************************************************************
The DBA Toolbox has been deployed. Kindly ensure that the latest version of the
SQL Server Maintenance Solution (scripts for running backups, integrity checks,
and index and statistics maintenance) is downloaded from https://ola.hallengren.com/
and applied to the DBAToolbox database.
********************************************************************************';
PRINT '';
At the time of writing the objects are the following:
- Table/s
- CommandLog
- Stored Procedure/s
- CommandExecute
- DatabaseBackup
- DatabaseIntegrityCheck
- IndexOptimize
The next variables which might need to be modified are the following:
SET @CreateJobs = 'N' -- Specify whether jobs should be created.
SET @BackupDirectory = NULL -- Specify the backup root directory. If no directory is specified, the default backup directory is used.
SET @CleanupTime = NULL -- Time in hours, after which backup files are deleted. If no time is specified, then no backup files are deleted.
The @CreateJobs accepts either of “Y” or “N” values and determines whether jobs will be created. The following SQL Agent jobs are created if the default value is not changed:
- CommandLog Cleanup
- DatabaseBackup - SYSTEM_DATABASES - FULL
- DatabaseBackup - USER_DATABASES - DIFF
- DatabaseBackup - USER_DATABASES - FULL
- DatabaseBackup - USER_DATABASES - LOG
- DatabaseIntegrityCheck - SYSTEM_DATABASES
- DatabaseIntegrityCheck - USER_DATABASES
- IndexOptimize - USER_DATABASES
- Output File Cleanup
- sp_delete_backuphistory
- sp_purge_jobhistory
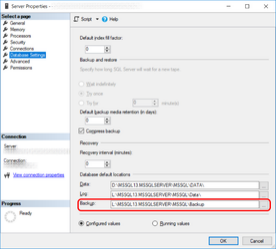
The value of the @BackupDirectory is the folder location where backups will be stored - this can be modified at a later stage to a custom location. If the default value of NULL is not set the solution will read the value defined during installation, or the one set in the Server Properties > Database default locations > Backup property as shown in the following screenshot:
The @CleanupTime variable determines the number of hours that should elapse before a backup file (Full, Differential or Transaction Log) can be deleted. If the default value of NULL is not changed this means that backups will not be deleted. It is imperative that this value aligns with the RPO value which the company would be contractually obliged to meet.
After the jobs have been created one would have to create schedules for each of these. The following can be used as a baseline.
- Daily every 10 minutes
- Mon to Sat @ 18:00
- Monthly on the 1st @ 09:00
- Weekly on Sat @ 19:00
- Weekly on Sun @ 07:00
- Weekly on Sun @ 18:00
Scripts to create and assign the above schedules to the default jobs are below.
Create Default Schedules
IF NOT EXISTS(SELECT 1 FROM msdb.dbo.sysschedules WHERE name = N'Daily every 10 minutes')
BEGIN
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_add_schedule
@schedule_name=N'Daily every 10 minutes',
@enabled=1,
@freq_type=4,
@freq_interval=1,
@freq_subday_type=4,
@freq_subday_interval=10,
@freq_relative_interval=0,
@freq_recurrence_factor=0,
@active_start_date=20190101,
@active_end_date=99991231,
@active_start_time=63000,
@active_end_time=175959;
END
GO
IF NOT EXISTS(SELECT 1 FROM msdb.dbo.sysschedules WHERE name = N'Mon to Sat @ 18:00')
BEGIN
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_add_schedule
@schedule_name=N'Mon to Sat @ 18:00',
@enabled=1,
@freq_type=8,
@freq_interval=126,
@freq_subday_type=1,
@freq_subday_interval=0,
@freq_relative_interval=0,
@freq_recurrence_factor=1,
@active_start_date=20190101,
@active_end_date=99991231,
@active_start_time=0,
@active_end_time=235959;
END
GO
IF NOT EXISTS(SELECT 1 FROM msdb.dbo.sysschedules WHERE name = N'Monthly on the 1st @ 09:00')
BEGIN
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_add_schedule
@schedule_name=N'Monthly on the 1st @ 09:00',
@enabled=1,
@freq_type=16,
@freq_interval=1,
@freq_subday_type=1,
@freq_subday_interval=0,
@freq_relative_interval=0,
@freq_recurrence_factor=1,
@active_start_date=20190101,
@active_end_date=99991231,
@active_start_time=90000,
@active_end_time=235959;
END
GO
IF NOT EXISTS(SELECT 1 FROM msdb.dbo.sysschedules WHERE name = N'Weekly on Sat @ 19:00')
BEGIN
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_add_schedule
@schedule_name=N'Weekly on Sat @ 19:00',
@enabled=1,
@freq_type=8,
@freq_interval=64,
@freq_subday_type=1,
@freq_subday_interval=0,
@freq_relative_interval=0,
@freq_recurrence_factor=1,
@active_start_date=20190101,
@active_end_date=99991231,
@active_start_time=190000,
@active_end_time=235959;
END
GO
IF NOT EXISTS(SELECT 1 FROM msdb.dbo.sysschedules WHERE name = N'Weekly on Sun @ 07:00')
BEGIN
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_add_schedule
@schedule_name=N'Weekly on Sun @ 07:00',
@enabled=1,
@freq_type=8,
@freq_interval=1,
@freq_subday_type=1,
@freq_subday_interval=0,
@freq_relative_interval=0,
@freq_recurrence_factor=1,
@active_start_date=20190101,
@active_end_date=99991231,
@active_start_time=70000,
@active_end_time=235959;
END
GO
IF NOT EXISTS(SELECT 1 FROM msdb.dbo.sysschedules WHERE name = N'Weekly on Sun @ 18:00')
BEGIN
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_add_schedule
@schedule_name=N'Weekly on Sun @ 18:00',
@enabled=1,
@freq_type=8,
@freq_interval=1,
@freq_subday_type=1,
@freq_subday_interval=0,
@freq_relative_interval=0,
@freq_recurrence_factor=1,
@active_start_date=20190101,
@active_end_date=99991231,
@active_start_time=180000,
@active_end_time=235959;
END
GO
Map Jobs to the Default Schedules
-- Map Jobs to Schedules
SET NOCOUNT ON;
DECLARE @JobName nvarchar(250);
DECLARE @ScheduleName nvarchar(250);
DECLARE @JobID uniqueidentifier;
DECLARE @ScheduleID int;
DECLARE @JobSchedules TABLE (JobName nvarchar(250), ScheduleName nvarchar(250));
-- default job schedule mapping
INSERT INTO @JobSchedules (JobName, ScheduleName)
SELECT N'CommandLog Cleanup', N'Monthly on the 1st @ 09:00' UNION ALL
SELECT N'DatabaseBackup - SYSTEM_DATABASES - FULL', N'Weekly on Sun @ 18:00' UNION ALL
SELECT N'DatabaseBackup - USER_DATABASES - DIFF', N'Mon to Sat @ 18:00' UNION ALL
SELECT N'DatabaseBackup - USER_DATABASES - FULL', N'Weekly on Sun @ 18:00' UNION ALL
SELECT N'DatabaseBackup - USER_DATABASES - LOG', N'Daily every 10 minutes' UNION ALL
SELECT N'DatabaseIntegrityCheck - SYSTEM_DATABASES', N'Weekly on Sun @ 07:00' UNION ALL
SELECT N'DatabaseIntegrityCheck - USER_DATABASES', N'Weekly on Sun @ 07:00' UNION ALL
SELECT N'IndexOptimize - USER_DATABASES', N'Weekly on Sat @ 19:00' UNION ALL
SELECT N'Output File Cleanup', N'Monthly on the 1st @ 09:00' UNION ALL
SELECT N'sp_delete_backuphistory', N'Monthly on the 1st @ 09:00' UNION ALL
SELECT N'sp_purge_jobhistory', N'Monthly on the 1st @ 09:00';
-- create the mapping
DECLARE curJobSchedules CURSOR FOR
SELECT JobName, ScheduleName FROM @JobSchedules;
OPEN curJobSchedules
FETCH NEXT FROM curJobSchedules INTO @JobName, @ScheduleName;
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
SET @JobID = (SELECT job_id FROM msdb.dbo.sysjobs WHERE name = @JobName);
SET @ScheduleID = (SELECT schedule_id FROM msdb.dbo.sysschedules WHERE name = @ScheduleName);
IF ((@JobID IS NOT NULL) AND (@ScheduleID IS NOT NULL))
BEGIN
IF NOT EXISTS(SELECT 1 FROM msdb.dbo.sysjobschedules WHERE job_id = @JobID and schedule_id = @ScheduleID)
BEGIN
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_attach_schedule @job_id=@JobID,@schedule_id=@ScheduleID;
END
END
ELSE
BEGIN
PRINT 'Could not associate schedule "' + @ScheduleName + '" with job "' + @JobName + '"';
END
FETCH NEXT FROM curJobSchedules INTO @JobName, @ScheduleName;
END
CLOSE curJobSchedules;
DEALLOCATE curJobSchedules;
GO
The following supplementary script can be used to generate the creation of schedules:
Reverse Engineer Schedule Creation
SET NOCOUNT ON;
SELECT
'IF NOT EXISTS(SELECT 1 FROM msdb.dbo.sysschedules WHERE name = N''' + name + ''')
BEGIN
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_add_schedule
@schedule_name=N''' + name + ''',
@enabled=' + CAST(enabled AS char(1)) + ',
@freq_type=' + CAST(freq_type AS varchar(5)) + ',
@freq_interval=' + CAST(freq_interval AS varchar(5)) + ',
@freq_subday_type=' + CAST(freq_subday_type AS varchar(5)) + ',
@freq_subday_interval=' + CAST(freq_subday_interval AS varchar(5)) + ',
@freq_relative_interval=' + CAST(freq_relative_interval AS varchar(5)) + ',
@freq_recurrence_factor=' + CAST(freq_recurrence_factor AS varchar(5)) + ',
@active_start_date=' + CAST(active_start_date AS varchar(8)) + ',
@active_end_date=' + CAST(active_end_date AS varchar(8)) + ',
@active_start_time=' + CAST(active_start_time AS varchar(8)) + ',
@active_end_time=' + CAST(active_end_time AS varchar(8)) + ';
END
GO'
FROM msdb.dbo.sysschedules
WHERE name IN (
N'Daily every 10 minutes',
N'Mon to Sat @ 18:00',
N'Monthly on the 1st @ 09:00',
N'Weekly on Sat @ 19:00',
N'Weekly on Sun @ 07:00',
N'Weekly on Sun @ 18:00'
)
ORDER BY name;
Of course one could decide to create jobs specific to fine-tune the processes, customer requirements, or different retention periods for example. The documentation at https://ola.hallengren.com/ would assist in this task.