Accurate documentation is paramount for any system. Unfotunately, when developing a database we sometimes tend to overlook this particular document.
A data dictionary shows metadata about your database. This information can be generated from the DBMS itself using the INFORMATION_SCHEMA compatibility views. Information such as the list of tables, table columns, views, stored procedures, and more can be extracted using the below queries and stored in a document to serve as a snapshot or say, to distribute to developers.
So, for example, to extract the list of tables in the current database, we can execute the following query:
-- tables
SELECT table_catalog, table_schema, table_name
FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES
WHERE table_name NOT IN ('sysconstraints', 'syssegments')
AND TABLE_TYPE = 'BASE TABLE'
ORDER BY table_catalog, table_schema, table_name;
A list of views can be retrieved by executing:
-- views
SELECT table_catalog, table_schema, table_name AS view_name, is_updatable
FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.VIEWS
WHERE table_name NOT IN ('sysconstraints', 'syssegments')
ORDER BY table_catalog, table_schema, table_name;
The table columns and some of the attributes can be retrieved using:
-- table columns
SELECT
table_catalog, table_schema, table_name, column_name, ordinal_position, �
data_type,
[length/precision] =
CASE data_type
WHEN 'char' THEN (CASE ISNULL(character_maximum_length, 0) WHEN 0 THEN '' WHEN -1 THEN 'MAX' ELSE CONVERT(VARCHAR(10), character_maximum_length) END)
WHEN 'nchar' THEN (CASE ISNULL(character_maximum_length, 0) WHEN 0 THEN '' WHEN -1 THEN 'MAX' ELSE CONVERT(VARCHAR(10), character_maximum_length) END)
WHEN 'varchar' THEN (CASE ISNULL(character_maximum_length, 0) WHEN 0 THEN '' WHEN -1 THEN 'MAX' ELSE CONVERT(VARCHAR(10), character_maximum_length) END)
WHEN 'nvarchar' THEN (CASE ISNULL(character_maximum_length, 0) WHEN 0 THEN '' WHEN -1 THEN 'MAX' ELSE CONVERT(VARCHAR(10), character_maximum_length) END)
WHEN 'numeric' THEN (CASE ISNULL(numeric_precision, 0) WHEN 0 THEN '' ELSE CONVERT(VARCHAR(10), numeric_precision) + ', ' + CONVERT(VARCHAR(10), numeric_scale) END)
WHEN 'decimal' THEN (CASE ISNULL(numeric_precision, 0) WHEN 0 THEN '' ELSE CONVERT(VARCHAR(10), numeric_precision) + ', ' + CONVERT(VARCHAR(10), numeric_scale) END)
ELSE ''
END
FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.Columns
WHERE table_name NOT IN ('sysconstraints', 'syssegments')
ORDER BY table_catalog, table_schema, table_name, ordinal_position;
Stored procedeures and functions’ information is generated using:
-- stored procedures and functions
SELECT
routine_catalog, routine_schema, routine_name, routine_type,
[return_data_type] =
CASE ISNULL(data_type, '')
WHEN 'char' THEN (CASE ISNULL(character_maximum_length, 0) WHEN 0 THEN '' WHEN -1 THEN data_type + ' (MAX)' ELSE data_type + ' (' + CONVERT(VARCHAR(10), character_maximum_length) + ')' END)
WHEN 'nchar' THEN (CASE ISNULL(character_maximum_length, 0) WHEN 0 THEN '' WHEN -1 THEN data_type + ' (MAX)' ELSE data_type + ' (' + CONVERT(VARCHAR(10), character_maximum_length) + ')' END)
WHEN 'varchar' THEN (CASE ISNULL(character_maximum_length, 0) WHEN 0 THEN '' WHEN -1 THEN data_type + ' (MAX)' ELSE data_type + ' (' + CONVERT(VARCHAR(10), character_maximum_length) + ')' END)
WHEN 'nvarchar' THEN (CASE ISNULL(character_maximum_length, 0) WHEN 0 THEN '' WHEN -1 THEN data_type + ' (MAX)' ELSE data_type + ' (' + CONVERT(VARCHAR(10), character_maximum_length) + ')' END)
ELSE ISNULL(data_type, '')
END
FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.routines
ORDER BY routine_catalog, routine_schema, routine_name;
And the final example will generate the stored procedure and function input and output parameters for the current database:
-- stored procedure and function parameters
SELECT
specific_catalog, specific_schema, specific_name,
parameter_name,
[length/precision] =
CASE data_type
WHEN 'char' THEN (CASE ISNULL(character_maximum_length, 0) WHEN 0 THEN '' WHEN -1 THEN 'MAX' ELSE CONVERT(VARCHAR(10), character_maximum_length) END)
WHEN 'nchar' THEN (CASE ISNULL(character_maximum_length, 0) WHEN 0 THEN '' WHEN -1 THEN 'MAX' ELSE CONVERT(VARCHAR(10), character_maximum_length) END)
WHEN 'varchar' THEN (CASE ISNULL(character_maximum_length, 0) WHEN 0 THEN '' WHEN -1 THEN 'MAX' ELSE CONVERT(VARCHAR(10), character_maximum_length) END)
WHEN 'nvarchar' THEN (CASE ISNULL(character_maximum_length, 0) WHEN 0 THEN '' WHEN -1 THEN 'MAX' ELSE CONVERT(VARCHAR(10), character_maximum_length) END)
WHEN 'numeric' THEN (CASE ISNULL(numeric_precision, 0) WHEN 0 THEN '' ELSE CONVERT(VARCHAR(10), numeric_precision) + ', ' + CONVERT(VARCHAR(10), numeric_scale) END)
WHEN 'decimal' THEN (CASE ISNULL(numeric_precision, 0) WHEN 0 THEN '' ELSE CONVERT(VARCHAR(10), numeric_precision) + ', ' + CONVERT(VARCHAR(10), numeric_scale) END)
ELSE ''
END,
ordinal_position, parameter_mode, is_result
FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.parameters
ORDER BY specific_catalog, specific_schema, specific_name, ordinal_position;
The below diagram shows the relationships between the INFORMATION_SCHEMA objects.
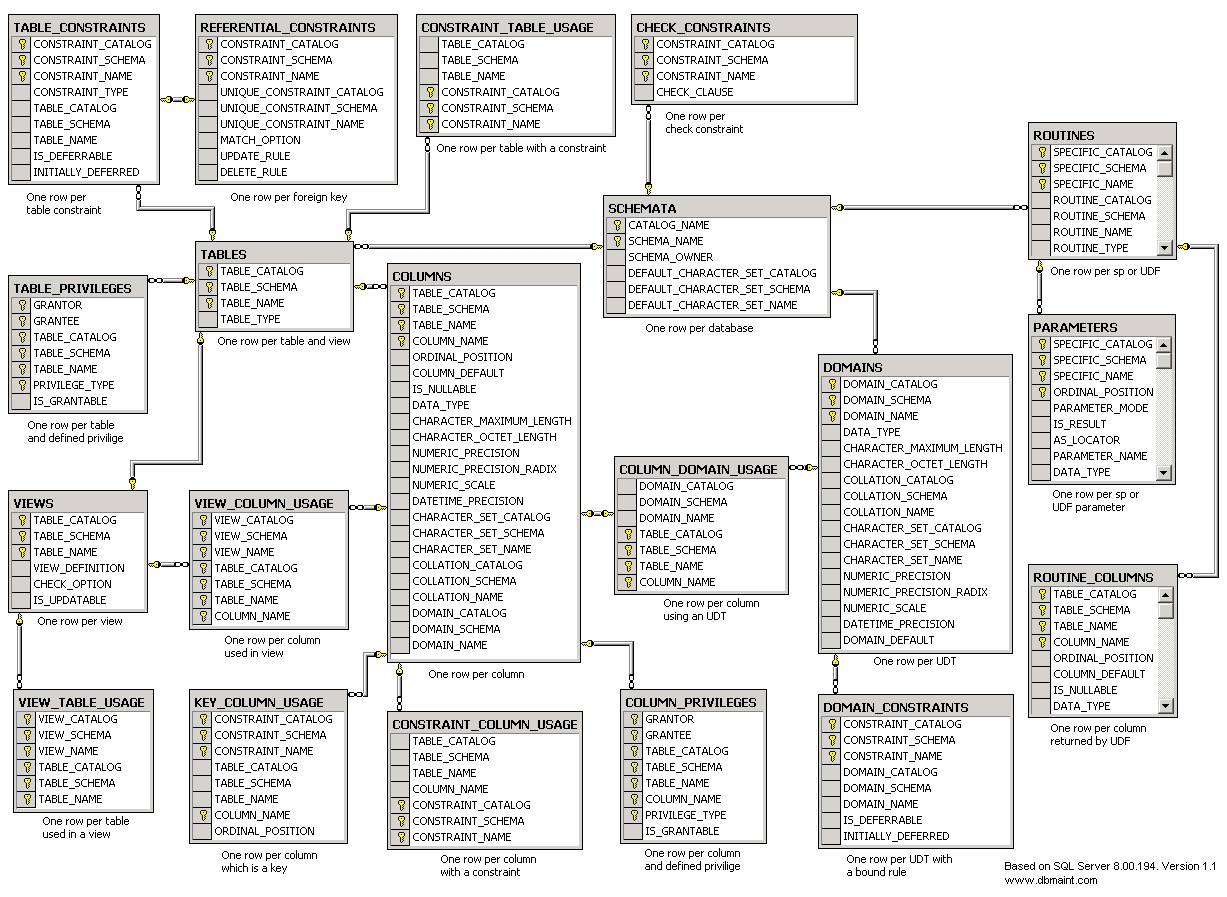
For more information about the INFORMATION_SCHEMA compatibility views and which other information can be retrieved can be found in the SQL Server Books Online at SQL Server Books Online.